In the process of finding effective weight loss solutions, one overlooked food is edamame. Our newest blog post addresses the critical question: “Is Edamame Good for Weight Loss?”
Here, we reveal how incorporating edamame into your diet can transform your approach to weight loss, providing a combination of essential nutrients without compromising on taste. Join us in discovering the hidden potential of this green food in your weight loss journey.
Read more
- Is Collard Greens Good for Weight Loss? Nutritional Information.
- Do Carrots Help You Lose Weight? The Superfood Secret.
- Are Brussels Sprouts Good for Weight Loss? Diet Benefits.
Is Edamame Good for Weight Loss?
Edamame, which is just young soybeans, can be really good for you if you’re trying to lose weight. It’s packed with protein and fiber, which help you manage your weight better. Studies show that soybeans are great for heart health too, especially because they help reduce swelling in the body, a common problem for people who are overweight.

What’s great about edamame is that it’s a plant protein, so it doesn’t have the unhealthy fats you find in meat. This is really important for keeping your heart healthy and keeping your cholesterol in check. Eating more plant proteins like edamame, instead of fatty meats, is really good for your heart. A study in the Journal of the American Heart Association even found that plant proteins can lower the bad kind of cholesterol (LDL cholesterol). Since being overweight can make cholesterol problems worse, eating edamame can help you lose weight and lower your cholesterol at the same time.
Nutrients Found in Edamame
Edamame is a superfood filled with vitamins and minerals that help fight diseases. It’s also rich in antioxidants, which protect your body from oxidative stress and damage caused by free radicals. These free radicals are bad news because they can speed up aging, lead to diseases, and make you feel low on energy. Plus, the vitamins in edamame are great for boosting your immune system. Here’s what you get in edamame:
- Vitamin A: Good for your eyes and skin.
- Vitamin C: Helps your body heal and absorb iron.
- Vitamin E: Protects your cells from damage.
- Vitamin K: Important for blood clotting and bone health.
- Calcium: Keeps your bones and teeth strong.
- Folate: Essential for pregnant women and general cell growth.
- Copper: Helps your body make energy and blood vessels.
- Magnesium: Good for muscle and nerve function.
- Manganese: Helps with bone formation and blood clotting.
- Potassium: Important for heart function and muscle contractions.
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): Helps your body break down food for energy.
- Thiamine (Vitamin B1): Helps your body turn food into energy.
- Zinc: Boosts your immune system and helps wounds heal.
All these nutrients make edamame a great choice for a healthy snack or addition to your meals.
Ways Edamame Facilitates Weight Loss
Edamame is a great food for weight loss because it’s full of protein and fiber. Just a half-cup serving gives you almost 8 grams of protein, which is 16% of what you need in a day if you’re following a 2,000-calorie diet. Protein is great for weight loss because it keeps you feeling full longer by slowing down how quickly your stomach empties after eating. Fiber also helps you feel full, which means you might end up eating less overall. Plus, edamame is low in calories – there’s only 95 calories in a half-cup, making it an ideal snack for those trying to lose weight.

Edamame isn’t just about protein and fiber; it’s packed with essential nutrients that are important for a healthy diet. It’s rich in omega-3 fatty acids, iron, zinc, vitamin C, folate, and vitamin E. All of these nutrients play a role in overall health and can support your weight loss efforts. By adding edamame to your daily meals, you’re making a smart choice for both weight management and nutrition.
Additional Advantages of Edamame
Edamame offers a wealth of health benefits beyond just being a delicious snack or appetizer:
Supports Cardiovascular Well-being
Rich in protein, edamame beans are good for heart health. A study in the New England Journal of Medicine found that replacing animal protein with soy protein improved blood lipid levels, reducing the risk of heart disease.
The high fiber content in edamame beans also helps reduce cholesterol and prevent the buildup of fatty plaque in the arteries.

Linked to Lowered Cancer Risk
Soy products like edamame might protect against certain cancers. Research suggests a lower risk of prostate cancer in men and potentially reduced breast cancer risk, though more studies are needed.
Exceptional Protein Content
Edamame is packed with plant-based protein, with a single serving containing about 17 grams. This protein is vital for tissue repair, muscle growth, immune function, and can help with weight loss by keeping you full longer.
Enhances Bone Strength
High in soy isoflavones, edamame boosts bone health. These isoflavones can improve bone metabolism and increase bone mineral density, especially beneficial for menopausal women.
Eases Menopausal Symptoms
Edamame contains soy isoflavones, which are classified as phytoestrogens. These compounds have the ability to replicate estrogen’s effects in the body.
Consequently, they might offer advantages for women experiencing menopause—a natural phase signifying the cessation of reproductive capabilities, characterized by a decrease in hormone levels.
Helps Maintain Stable Blood Sugar Levels
Edamame, like other legumes, is excellent for blood sugar control. It has a low glycemic index and is fiber-rich, which slows sugar absorption.
Studies have shown that soy isoflavones can significantly reduce blood sugar and insulin levels in postmenopausal women.
Potential Dangers and Adverse Effects of Edamame
While edamame is a nutritious food with many benefits, there are some potential downsides and side effects to consider:
Soy Allergy Concerns: Edamame is made from immature soybeans, so it’s not suitable for those with a soy allergy.
- Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs): A large percentage of soybeans in the U.S. are genetically engineered. Some people choose to avoid GMOs due to concerns about long-term health effects, antibiotic resistance, and food allergies. To reduce GMO exposure, you can opt for organic edamame.
- Antinutrients Content: Soybeans contain antinutrients, which can hinder the body’s ability to absorb certain minerals. However, soaking, sprouting, fermenting, or cooking edamame can significantly lower these antinutrients.
- Goitrogens and Thyroid Function: Soy contains goitrogens, compounds that might interfere with thyroid function by blocking iodine absorption. But, research indicates that soy products generally don’t affect thyroid function in healthy adults, unless there’s also an iodine deficiency.
- Carbohydrate Content for Low-Carb Diets: Although edamame is low in carbs and high in fiber, those on a keto or low-carb diet should be mindful of their intake to maintain a low carb consumption.

Is Edamame Pasta Good for Weight Loss?
Yes, edamame pasta can be a good choice for weight loss. Its high protein content is a major benefit, as protein can help you feel full and satisfied after meals, which might lead to eating less overall. Protein is also key for muscle repair and maintenance, especially if you’re combining your weight loss efforts with exercise.
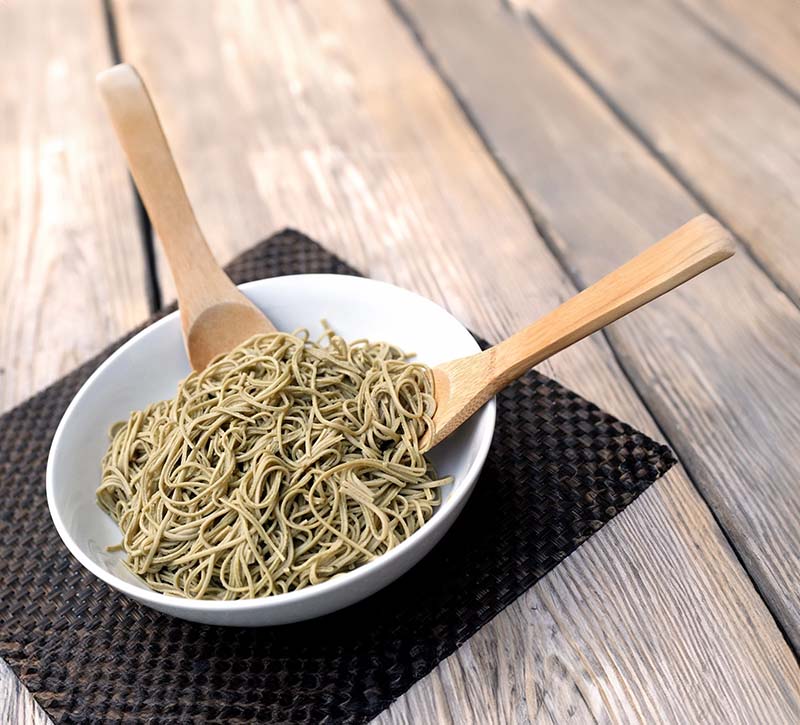

Moreover, edamame pasta is rich in fiber, which is crucial for good digestion. Fiber helps to regulate your digestive system and can prevent constipation. It also plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels, which is particularly important for people managing diabetes or those who are pre-diabetic. By stabilizing blood sugar levels, high-fiber foods like edamame pasta can prevent the spikes and drops that might lead to cravings and overeating.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the answer to “Is Edamame Good for Weight Loss?” is a resounding yes. This versatile, nutrient-packed green bean offers a multitude of health benefits, making it an ideal choice for anyone looking to manage their weight without sacrificing flavor. We encourage you to share your own experiences with edamame in your weight loss journey.
Have you found creative ways to include it in your meals, or noticed any significant changes in your health and well-being? Your stories can inspire and motivate others! Don’t forget to explore more insightful and health-focused content on Sure Life Health‘s blog, where we continuously unravel the secrets to a healthier, happier life.
Professor Gaye Cunnane, PhD, MB, FRCPI
As the Director of Health and Wellbeing at RCPI, Professor Gaye Cunnane is at the helm of initiatives aimed at enhancing the health and well-being of RCPI Trainers and Trainees. Her role extends beyond administration; she is also a respected clinical professor of rheumatology and a consultant rheumatologist at Trinity College Dublin (TCD) and St James’s Hospital. Prof. Cunnane’s medical journey began at TCD, where she graduated from medical school, and her path has been marked by both clinical and academic excellence.
After completing her basic clinical training in medicine, she embarked on PhD studies at University College Dublin and St Vincent’s University Hospital. Her research during this period was focused on prognostic markers in early inflammatory arthritis, a project that saw her collaborating with esteemed universities across Europe, including in Switzerland, The Netherlands, the UK, and Sweden.
Prof. Cunnane’s career took her to the University of California, San Francisco, where she spent three years delving into research on new treatments for lupus. Her academic prowess led her to the University of Leeds in 2001 as a senior lecturer, before returning to Ireland in 2003 to assume her current roles. She has also served as the National Specialty Director for Rheumatology training in Ireland, Programme Director for Basic Specialist Training with RCPI, and as a past President of the Irish Society for Rheumatology.
PUBLISHED ARTICLES
“Rheumatic disease differentiation using immunoglobulin G sugar printing by high-density electrophoresis”: Published in The Journal of Rheumatology, this study reflects her in-depth investigation into rheumatic diseases.
“Benefits of exercise in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial”: This research work, highlighting the positive impact of exercise on rheumatoid arthritis, underscores Prof. Cunnane’s dedication to practical, patient-centered research.
Additionally, Prof. Cunnane has made notable contributions to the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, discussing early referral, diagnosis, and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. She has also been involved in a study on the NCBI platform investigating exercise benefits in rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Professor Gaye Cunnane’s career is a testament to her commitment to improving patient outcomes in rheumatology through rigorous research, clinical excellence, and dedicated teaching. Her work continues to influence the field of rheumatology, both in Ireland and internationally.

