Beetroot powder and beet juice stand out in the world of nutrition as a remarkable, natural way to enhance physical performance and stamina. This isn’t just an ordinary supplement; it’s a powerhouse derived from the mother nature with the potential to transform your body’s capabilities.
When you incorporate beetroot into your diet, you’re not just adding a nutrient-rich food. You’re unlocking a natural mechanism that boosts the flow of blood and oxygen throughout your body, empowering you with increased endurance and energy.
Join us on this vibrant voyage to uncover the mystery, the science, and the allure behind beetroot powder’s crimson power!
Beetroot Powder Benefits for Men
Beetroot powder offers several health perks specifically tailored for men. Here’s a breakdown of the benefits:
Helps Reduce Blood Pressure
Research suggests that beetroot can help lower blood pressure. Low levels of nitric oxide may contribute to endothelial dysfunction, a major risk factor for cardiovascular issues like high blood pressure and artery hardening.
Multiple studies have linked beetroot consumption to cardiovascular benefits such as reduced blood pressure, enhanced muscle oxygenation, and more flexible blood vessels.
Supports Anti-inflammation
Some evidence indicates that beetroot possesses anti-inflammatory properties. A study involving arthritis patients showed that supplementing with beetroot for just 10 days led to decreased inflammatory markers and pain.
Similarly, a few studies in rats have shown positive results in reducing inflammation by using.

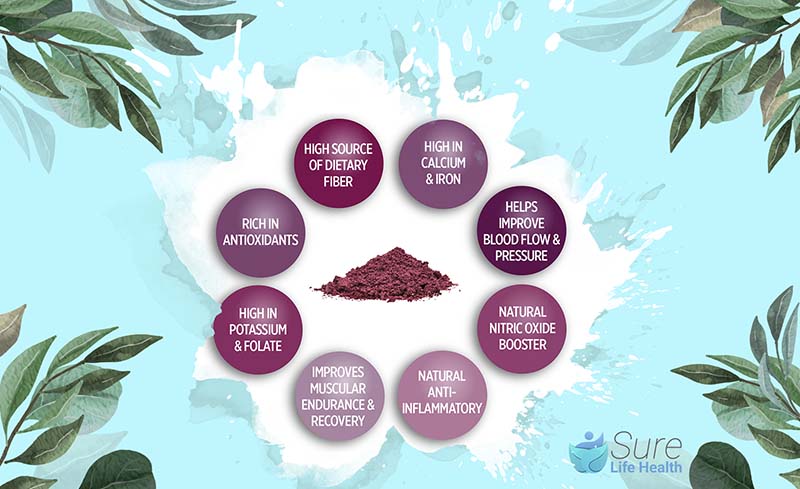
Contains Many Antioxidants
Beetroot is packed with various antioxidant compounds, including betalain, a pigment containing nitrogen.
Lab studies demonstrate that beetroot juice can shield against oxidative stress on various cell types, including fats, proteins, and DNA. Surprisingly, simulated digestion actually amplifies the antioxidant power of beetroot.

Helps Improve Nitric Oxide Production
Beetroot offers a significant advantage for vascular health through its high dietary nitrate content, which is converted into nitric oxide during digestion.
Nitric oxide is essential for maintaining the elasticity and health of the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels. As natural nitric oxide production decreases with age, incorporating beetroot into one’s diet can help counteract this decline, supporting optimal blood flow and vascular function.
This process underscores beetroot’s role not just as a nutrient-dense food, but as a strategic tool for sustaining cardiovascular health.
Incorporating beetroot powder into your routine can offer these advantages, promoting overall health and well-being for men.
Side Effects When Using Beetroot
When using beetroot, it’s crucial to be mindful of potential side effects:
- Kidney Stone Risk: Beetroot powder is rich in oxalates, which can contribute to the formation of kidney stones. If you’ve experienced the discomfort of passing a kidney stone before, it’s important to be cautious with beetroot consumption.
- Changes in Bodily Output: Consuming beetroot powder may cause noticeable changes in the color of your urine and stool. The vibrant red coloring of the supplement can impart a different hue to your bodily waste.
- Elevated Nitrate Levels: Overconsumption of beetroot juice can lead to increased blood levels of nitrates beyond recommended limits. This elevation may encourage the formation of N-nitroso compounds (NOCs), which could potentially have carcinogenic effects. However, more research is needed to fully understand this risk.
It’s advisable to consult with your healthcare provider before incorporating beetroot supplements into your routine, especially if you’re currently taking medications or managing a health condition. Your healthcare provider can offer personalized guidance based on your individual health needs and circumstances.

Who Should Not Use Beetroot Powder?
- Allergy to Beetroot: Individuals with an allergy to beetroot should avoid consuming beet powder. Allergic reactions may manifest as symptoms such as dizziness, rash, swelling (especially around the face and neck), coughing, difficulty breathing, and nausea/vomiting. If someone experiences difficulty breathing after consuming beetroot in any form, immediate medical attention is necessary.
- Low Blood Pressure: Individuals with low blood pressure should consult with their doctors before incorporating beetroot powder into their diet. This caution is due to beetroot powder’s capability to lower blood pressure levels further, which might not be suitable for those already managing low blood pressure.
Can Beets Help Treat Erectile Dysfunction?
The potential of beets in treating erectile dysfunction arises from their ability to enhance nitric oxide production, improve blood circulation to the penis, and protect the endothelium. While there’s anecdotal evidence supporting this notion, formal studies validating the direct link between beet consumption and improved erectile function are lacking.
Despite the absence of conclusive scientific evidence, given the numerous health benefits associated with beets, integrating them into your diet could be beneficial. Monitoring any changes in your body’s response can help assess the impact of beets on overall health, including potential effects on erectile function.
Other Alternative Foods
Several foods have been linked to potentially enhancing erections by improving circulation, boosting testosterone levels, and reducing inflammation. Here are some alternative options:
- Leafy Greens: Spinach and kale are packed with nitrates, which can be converted into nitric oxide in the body. Nitric oxide helps relax blood vessels, including those in the penis, leading to improved blood flow and potentially supporting erectile function.
- Watermelon: Watermelon contains citrulline, a compound known for its ability to relax blood vessels and enhance blood flow. Research from 2018 suggested that citrulline might help prevent erectile dysfunction.
- Pistachios: Pistachios are rich in antioxidants and healthy fats, which can promote cardiovascular health and nitric oxide production, potentially benefiting erectile function.
- Oysters and Shellfish: Oysters and other shellfish are known to boost testosterone levels due to their high zinc content, a nutrient crucial for testosterone production.
- Coffee: Coffee contains caffeine, which can stimulate blood flow and improve circulation. Some studies have hinted at a potential link between moderate caffeine consumption and improved erectile function, though more research is needed for confirmation.
- Dark Chocolate: Dark chocolate contains flavonoids, antioxidants that support cardiovascular health. Enhanced cardiovascular function can positively impact blood flow, potentially benefiting erectile function.
- Salmon: Salmon is a fatty fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which promote cardiovascular health, reduce inflammation, and enhance blood flow, indirectly supporting erectile function.
- Flaxseed Oil: Flaxseed oil is a source of alpha-linolenic acid, an omega-3 fatty acid known for its potential to promote cardiovascular health and enhance blood flow.
Incorporating these foods into your diet can contribute to overall health and potentially support erectile function. However, it’s essential to maintain a balanced diet and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and recommendations.
Beetroot Powder Dosage Per Day
Determining the optimal dosage of beetroot powder can be challenging due to varying recommendations across different products. Typically, suggested doses are provided on the product label, and these can vary significantly.
For instance, some products may advise consuming 3–6 grams of powder, while others may suggest 2–3 teaspoons. For beetroot juice products, particularly those targeted at athletes, manufacturers might recommend drinking around 140 milliliters per day.
Although the listed doses are generally considered safe, it’s crucial to consider individual factors such as age, existing health conditions, sex, and more. Consulting with a healthcare professional before incorporating beetroot powder into your regimen is highly recommended, especially if you’re taking other medications or managing health conditions. Your healthcare provider can offer personalized guidance to ensure safe and effective usage of beetroot powder.
Conclusion
In conclusion, beetroot powder presents itself as a versatile addition to one’s diet, offering a range of potential benefits. When consumed in moderation, it is generally considered a safe food supplement.
Despite numerous studies exploring its advantages, further research is warranted to fully understand the extent of beetroot powder’s efficacy in addressing chronic diseases, enhancing athletic performance, and promoting overall health.
Scientists are actively investigating the processes through which beetroot powder exerts its benefits and determining the ideal dosage for maximum advantage. As knowledge in this area grows, beetroot powder emerges as a potential key element in a health-oriented lifestyle.
Be sure to explore more insightful blogs from Sure Life Health, where we continue to shed light on the latest trends and breakthroughs in health and wellness.
Professor Gaye Cunnane, PhD, MB, FRCPI
As the Director of Health and Wellbeing at RCPI, Professor Gaye Cunnane is at the helm of initiatives aimed at enhancing the health and well-being of RCPI Trainers and Trainees. Her role extends beyond administration; she is also a respected clinical professor of rheumatology and a consultant rheumatologist at Trinity College Dublin (TCD) and St James’s Hospital. Prof. Cunnane’s medical journey began at TCD, where she graduated from medical school, and her path has been marked by both clinical and academic excellence.
After completing her basic clinical training in medicine, she embarked on PhD studies at University College Dublin and St Vincent’s University Hospital. Her research during this period was focused on prognostic markers in early inflammatory arthritis, a project that saw her collaborating with esteemed universities across Europe, including in Switzerland, The Netherlands, the UK, and Sweden.
Prof. Cunnane’s career took her to the University of California, San Francisco, where she spent three years delving into research on new treatments for lupus. Her academic prowess led her to the University of Leeds in 2001 as a senior lecturer, before returning to Ireland in 2003 to assume her current roles. She has also served as the National Specialty Director for Rheumatology training in Ireland, Programme Director for Basic Specialist Training with RCPI, and as a past President of the Irish Society for Rheumatology.
PUBLISHED ARTICLES
“Rheumatic disease differentiation using immunoglobulin G sugar printing by high-density electrophoresis”: Published in The Journal of Rheumatology, this study reflects her in-depth investigation into rheumatic diseases.
“Benefits of exercise in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial”: This research work, highlighting the positive impact of exercise on rheumatoid arthritis, underscores Prof. Cunnane’s dedication to practical, patient-centered research.
Additionally, Prof. Cunnane has made notable contributions to the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, discussing early referral, diagnosis, and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. She has also been involved in a study on the NCBI platform investigating exercise benefits in rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Professor Gaye Cunnane’s career is a testament to her commitment to improving patient outcomes in rheumatology through rigorous research, clinical excellence, and dedicated teaching. Her work continues to influence the field of rheumatology, both in Ireland and internationally.

