Green tea frequently appears in conversations about testosterone-boosting supplements, leading many to question its actual impact on testosterone levels.
Known for its health benefits, primarily due to its high antioxidant content, the direct effect of green tea on testosterone remains a topic of exploration.
In this article, we will explore the roles of green tea to uncover its potential impact on testosterone levels and its connection to overall hormone health.
Join us as we navigate through the scientific findings to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of green tea’s role in hormone regulation.

Does Green Tea Boost Testosterone?
Research into the effects of green tea on testosterone levels has yielded mixed findings. Some studies propose that green tea might help regulate testosterone levels by assisting in weight management and potentially increasing testosterone production if levels are low. Conversely, other research suggests that green tea could have adverse effects on testosterone production, particularly when consumed in high doses.
One reason for these conflicting results could be the presence of polyphenols, such as catechins, in green tea. These compounds have antioxidant properties and may influence testosterone production by reducing oxidative stress in the body. However, the precise mechanisms through which green tea polyphenols impact free testosterone levels remain unclear.
Overall, while there is some evidence to suggest a potential link between green tea and testosterone regulation, further research is necessary to fully understand the extent of this relationship and whether green tea genuinely boosts testosterone levels.
How Beneficial Is Green Tea in Increasing Testosterone?
Green tea can potentially benefit testosterone levels, primarily through its ability to aid weight loss. Excess body fat, often originating from obesity, is a significant contributor to declining testosterone levels in men. This excess fat slows down metabolic processes, impacting testosterone production.
Green tea contains catechins, which are compounds known to promote weight loss by enhancing fat metabolism and breaking down stubborn fat cells. Additionally, its anti-inflammatory properties can help prevent the storage of excess fat. Furthermore, the caffeine content in green tea can increase energy levels, which may lead to improved athletic performance and a faster fat-burning process.
Research indicates that reducing body fat can effectively boost testosterone output. Therefore, by assisting in weight management, green tea indirectly supports testosterone regulation. However, it’s important to note that while green tea may play a role in promoting weight loss and potentially influencing testosterone levels, individual responses can vary, and further research is needed to fully understand its impact on testosterone regulation.

What Effect Does Green Tea Have on Testosterone?
The impact of green tea on testosterone levels is a topic of ongoing research, with conflicting findings. Some research shows that green tea might help increase testosterone levels because it has substances called polyphenols, like catechins, which can lower oxidative stress in the body.
Lowering oxidative stress might help improve testosterone levels. One specific catechin in green tea, known as EGCG, might slow down an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase.
This enzyme changes testosterone into a different hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT). By slowing down this enzyme, green tea might help keep testosterone levels higher.
Additionally, the antioxidants in green tea could also help support testosterone by reducing oxidative stress. However, we need more studies to really understand how green tea affects testosterone levels.
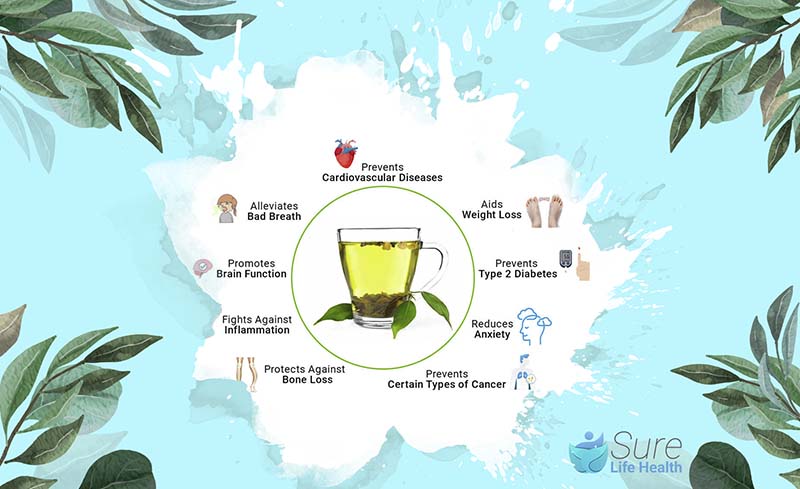
Other Benefits of Green Tea
Green tea offers a range of health benefits beyond its potential impact on testosterone levels. Here are some of the positive effects of green tea:
- Weight Loss: Green tea is renowned for its ability to assist in weight loss and fat metabolism, making it a preferred option for individuals aiming to manage their weight effectively.
- Antioxidant Properties: Rich in polyphenols like catechins and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), green tea acts as an antioxidant, helping to counteract oxidative stress and safeguard cells from damage.
- Anti-Inflammatory Benefits: The antioxidants present in green tea possess anti-inflammatory properties that may help alleviate inflammation in the body, contributing to overall health and well-being.
- Cancer Prevention: Some research indicates that components of green tea may inhibit the growth of tumor cells and potentially aid in cancer prevention, particularly concerning prostate cancer.
- Heart Health: Green tea is linked to cardiovascular benefits, including improvements in cholesterol levels, reduced risk of heart disease, and support for overall heart health.
- Immune System Support: The catechins found in green tea can bolster the immune system, assisting in combating certain bacteria and viruses, and regulating hormone production and activities.
- Hair Growth: Research suggests potential benefits of green tea for hair growth, with findings indicating positive effects on maintaining stable tissue testosterone levels and reducing the breakdown of testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
These diverse health advantages establish green tea as a favored choice for individuals seeking a natural means to enhance their overall well-being.
FAQs
Does Hibiscus Tea Increase Testosterone?
Research, primarily from animal studies, indicates that hibiscus may contribute to a decrease in testosterone levels.
Does Ginger Tea Increase Testosterone?
Evidence from various studies points to ginger potentially boosting testosterone levels, attributed to its antioxidant capabilities.
Does Chamomile Tea Increase Testosterone?
Current findings do not provide strong evidence to support a significant impact of chamomile tea on testosterone levels.
Does Rooibos Tea Increase Testosterone?
Research on the effects of rooibos tea on testosterone is insufficient, with the existing studies suggesting minimal hormonal effects.
Does Spearmint Tea Reduce Testosterone?
Spearmint tea is often associated with lower testosterone levels due to its potential to exhibit anti-androgenic properties.
Does Mint Tea Reduce Testosterone?
Mint tea has been linked to reduced testosterone levels in some studies, particularly due to its potential anti-androgen effects.
Does Black Tea Increase Testosterone?
Black tea has been associated with potential effects on testosterone levels. Studies suggest that black tea, particularly its polyphenols like theaflavins and epicatechin, may influence testosterone production.
Conclusion
In conclusion, despite the numerous health advantages attributed to green tea, evidence supporting its role in boosting testosterone levels is not adequate. Therefore, individuals seeking to enhance their testosterone levels should seek guidance from healthcare professionals and explore more established methods. Lifestyle changes and medically supervised treatments, such as Ashwagandha supplementation, are often more reliable for optimizing hormone levels.
The research underlines the significant role green tea may play in hormone regulation, specifically in how it interacts with other bioactive compounds in our diet.
This investigation into green tea’s potential effects on health, particularly hormone levels, broadens our comprehension of dietary impacts on bodily functions. This article provides a broader understanding of dietary influences on health and underscores how specific combinations of nutrients may have far-reaching implications for wellness and disease prevention.
Be sure to explore more insightful blogs from Sure Life Health, where we continue to shed light on the latest trends and breakthroughs in health and wellness.
Professor Gaye Cunnane, PhD, MB, FRCPI
As the Director of Health and Wellbeing at RCPI, Professor Gaye Cunnane is at the helm of initiatives aimed at enhancing the health and well-being of RCPI Trainers and Trainees. Her role extends beyond administration; she is also a respected clinical professor of rheumatology and a consultant rheumatologist at Trinity College Dublin (TCD) and St James’s Hospital. Prof. Cunnane’s medical journey began at TCD, where she graduated from medical school, and her path has been marked by both clinical and academic excellence.
After completing her basic clinical training in medicine, she embarked on PhD studies at University College Dublin and St Vincent’s University Hospital. Her research during this period was focused on prognostic markers in early inflammatory arthritis, a project that saw her collaborating with esteemed universities across Europe, including in Switzerland, The Netherlands, the UK, and Sweden.
Prof. Cunnane’s career took her to the University of California, San Francisco, where she spent three years delving into research on new treatments for lupus. Her academic prowess led her to the University of Leeds in 2001 as a senior lecturer, before returning to Ireland in 2003 to assume her current roles. She has also served as the National Specialty Director for Rheumatology training in Ireland, Programme Director for Basic Specialist Training with RCPI, and as a past President of the Irish Society for Rheumatology.
PUBLISHED ARTICLES
“Rheumatic disease differentiation using immunoglobulin G sugar printing by high-density electrophoresis”: Published in The Journal of Rheumatology, this study reflects her in-depth investigation into rheumatic diseases.
“Benefits of exercise in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized controlled trial”: This research work, highlighting the positive impact of exercise on rheumatoid arthritis, underscores Prof. Cunnane’s dedication to practical, patient-centered research.
Additionally, Prof. Cunnane has made notable contributions to the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, discussing early referral, diagnosis, and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. She has also been involved in a study on the NCBI platform investigating exercise benefits in rheumatoid arthritis patients.
Professor Gaye Cunnane’s career is a testament to her commitment to improving patient outcomes in rheumatology through rigorous research, clinical excellence, and dedicated teaching. Her work continues to influence the field of rheumatology, both in Ireland and internationally.

